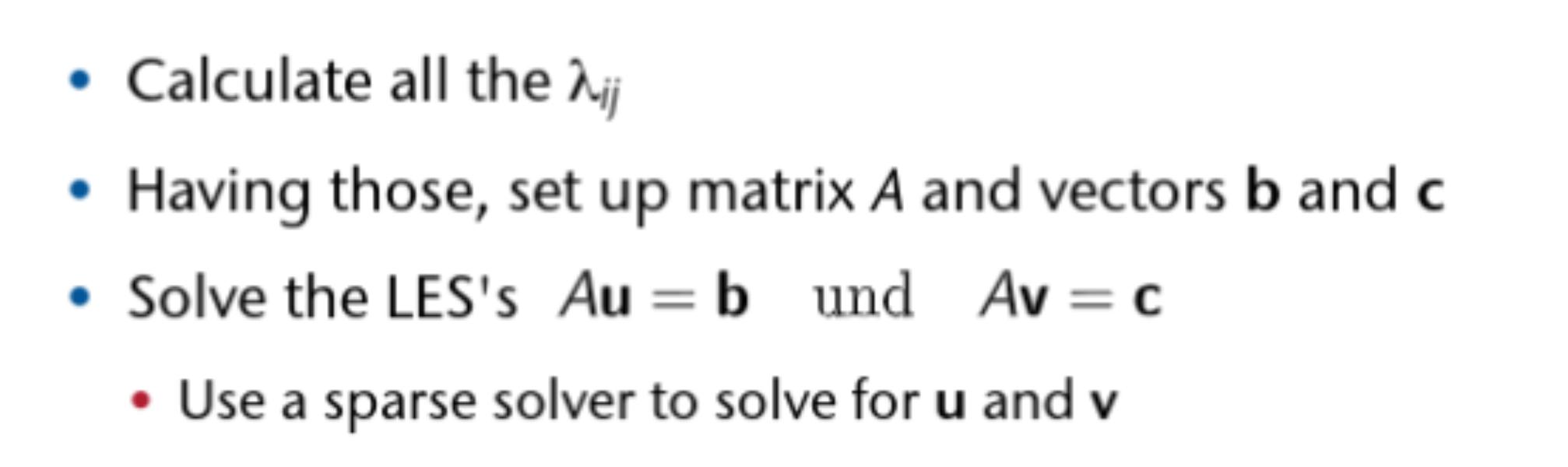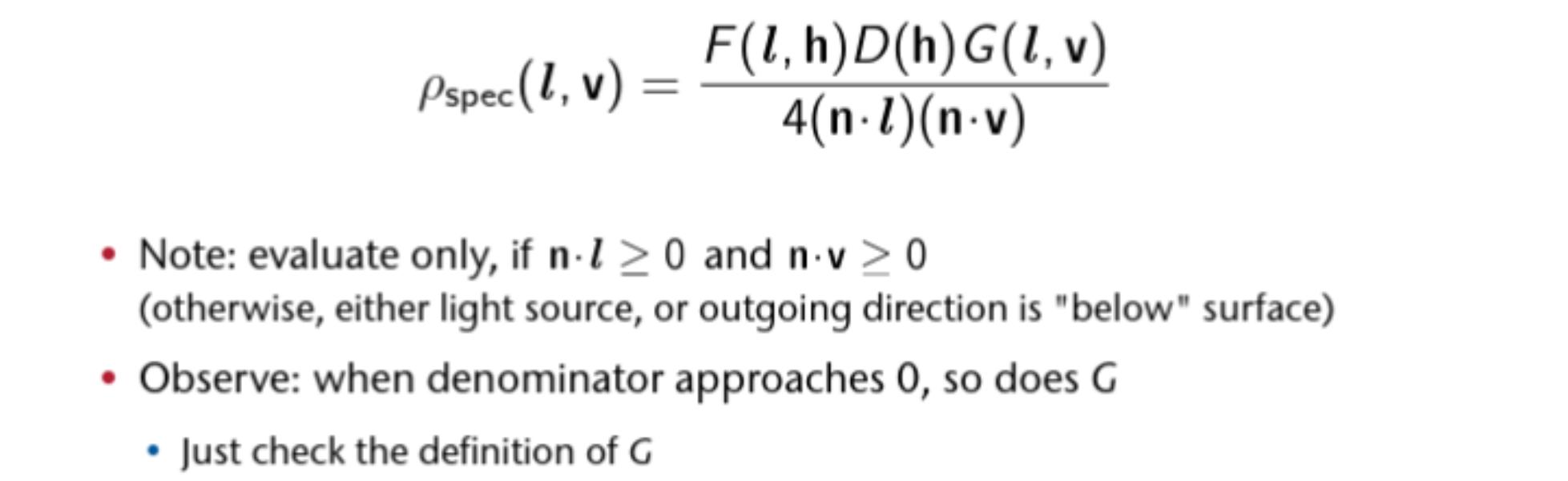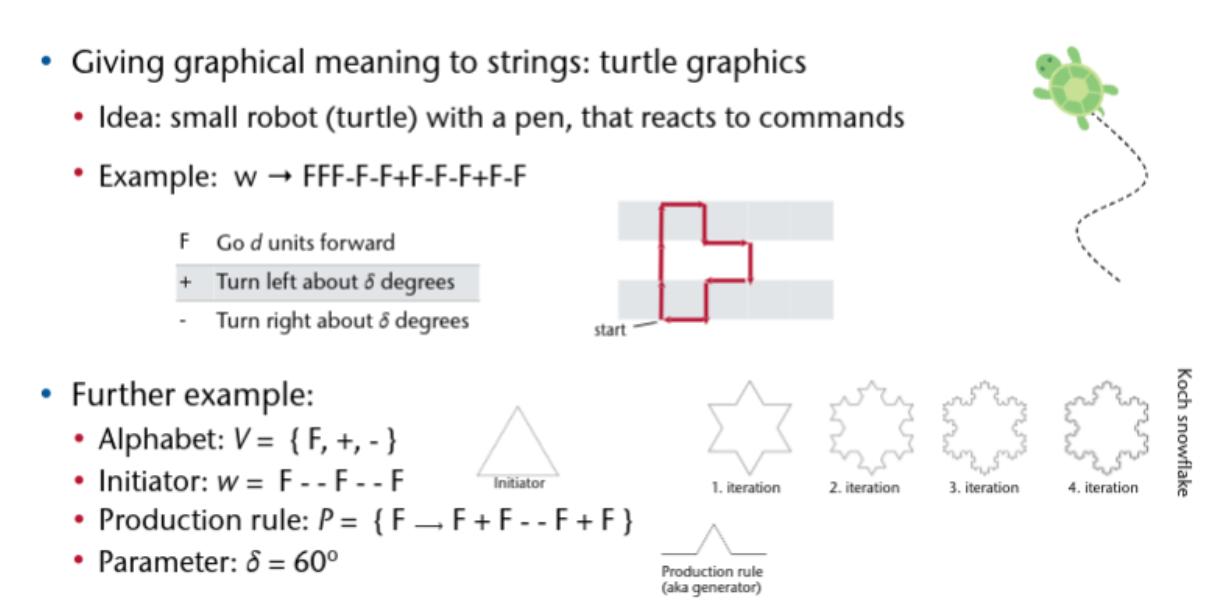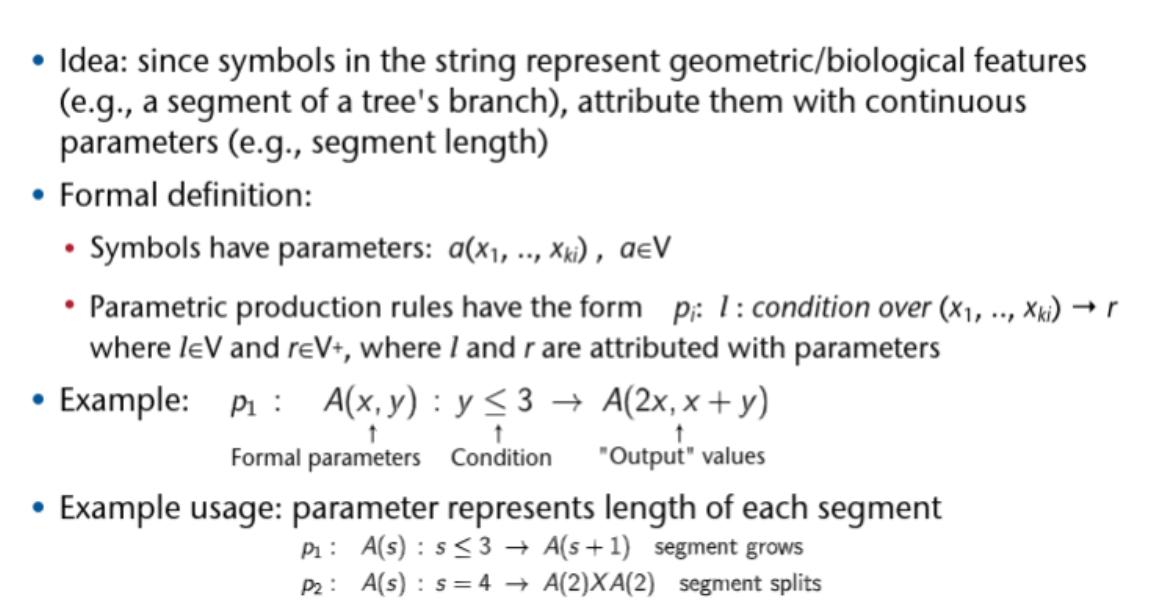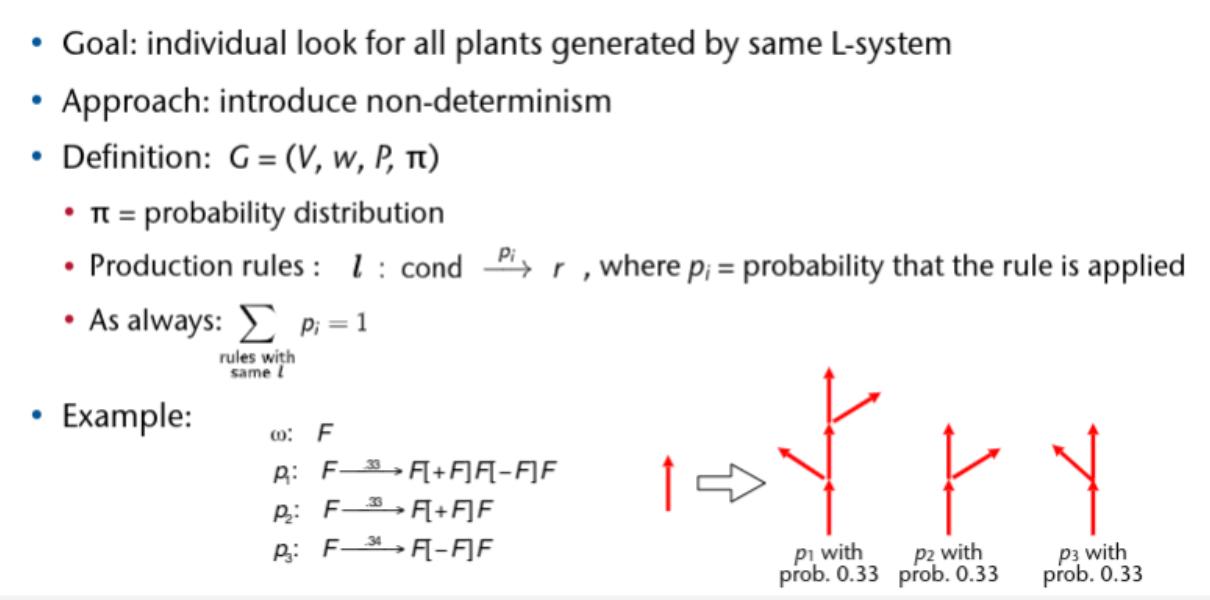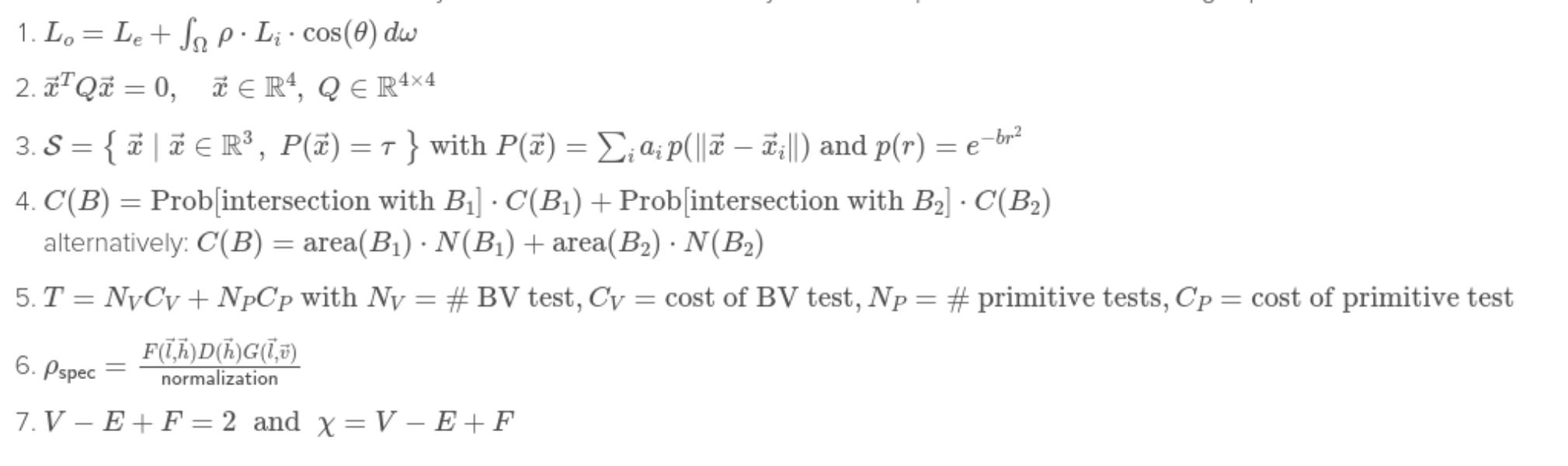
Raytracing
geometric algorithm to compute intersections of rays with the scene (aka. ray-based visibility)
-
Primary Rays
⇒ Camera Model -
Secondary rays and shadow feelers
⇒ Secondary Rays
→ Reflection and Refraction -
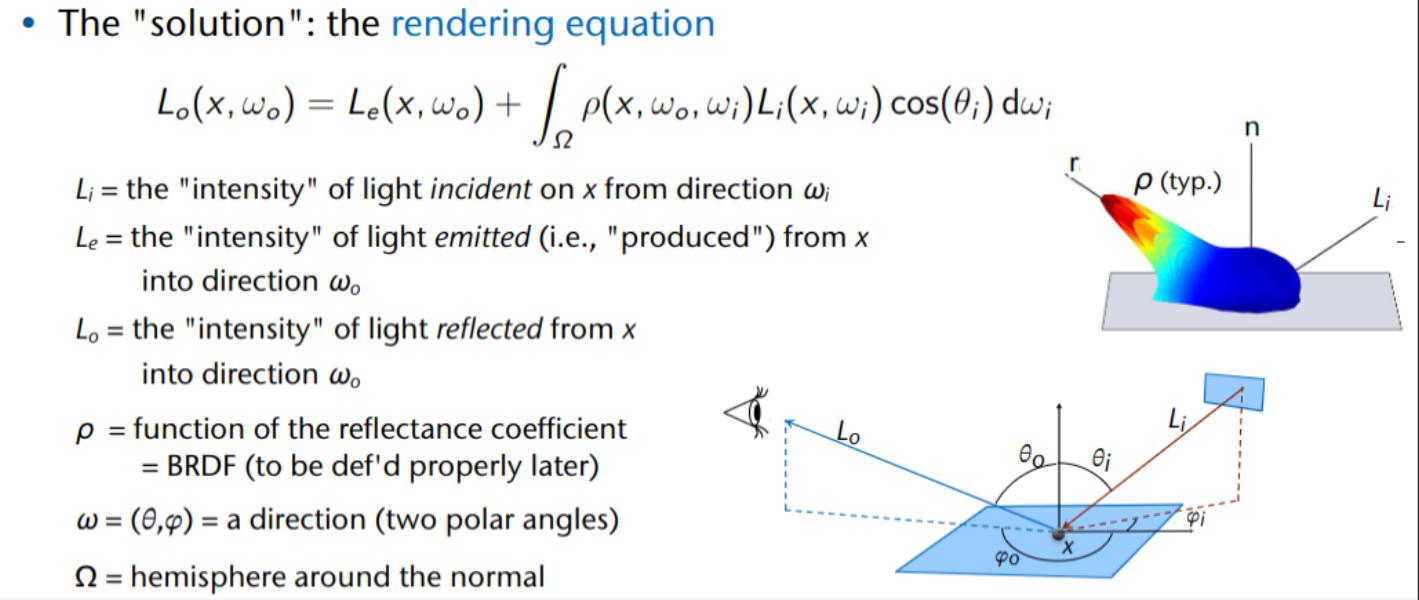
Combining all incoming light into “one” outgoing light
⇒ Lighting models


Pathtracing
Algorithm to compute global illumination by shooting rays in all kinds of (random) directions (aka. random sampling, aka. Monte Carlo integration)
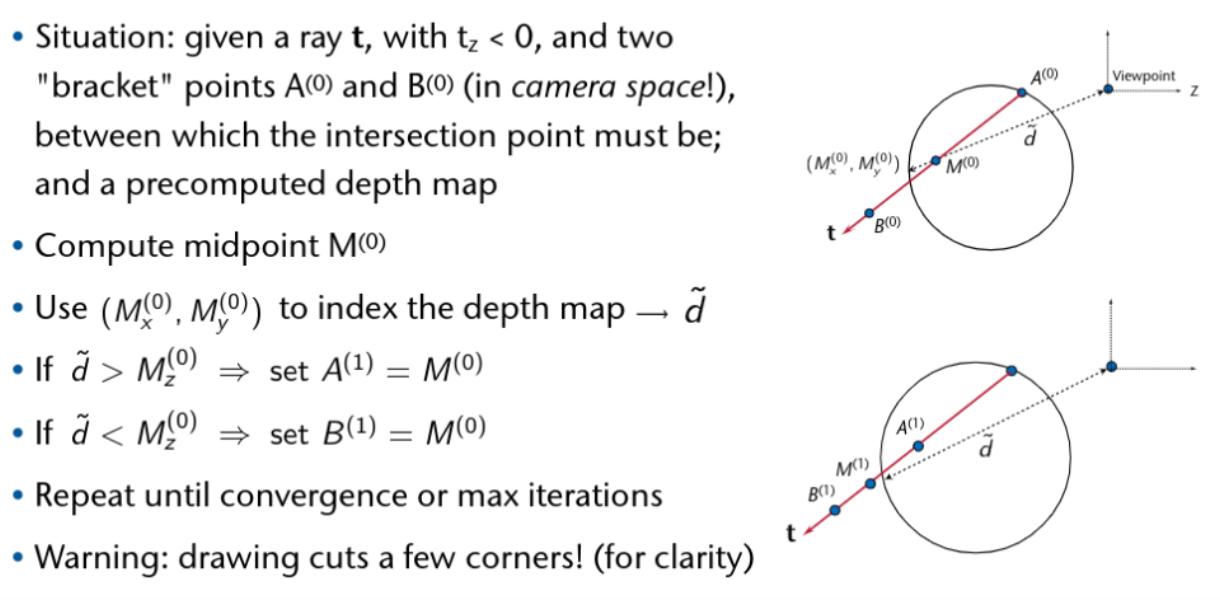
Intersection
Ray Triangle Intersection
Ray Box Intersection
Ray Sphere Intersection
Distribution Ray Tracing
⇒ Solution for Anti-Aliasing
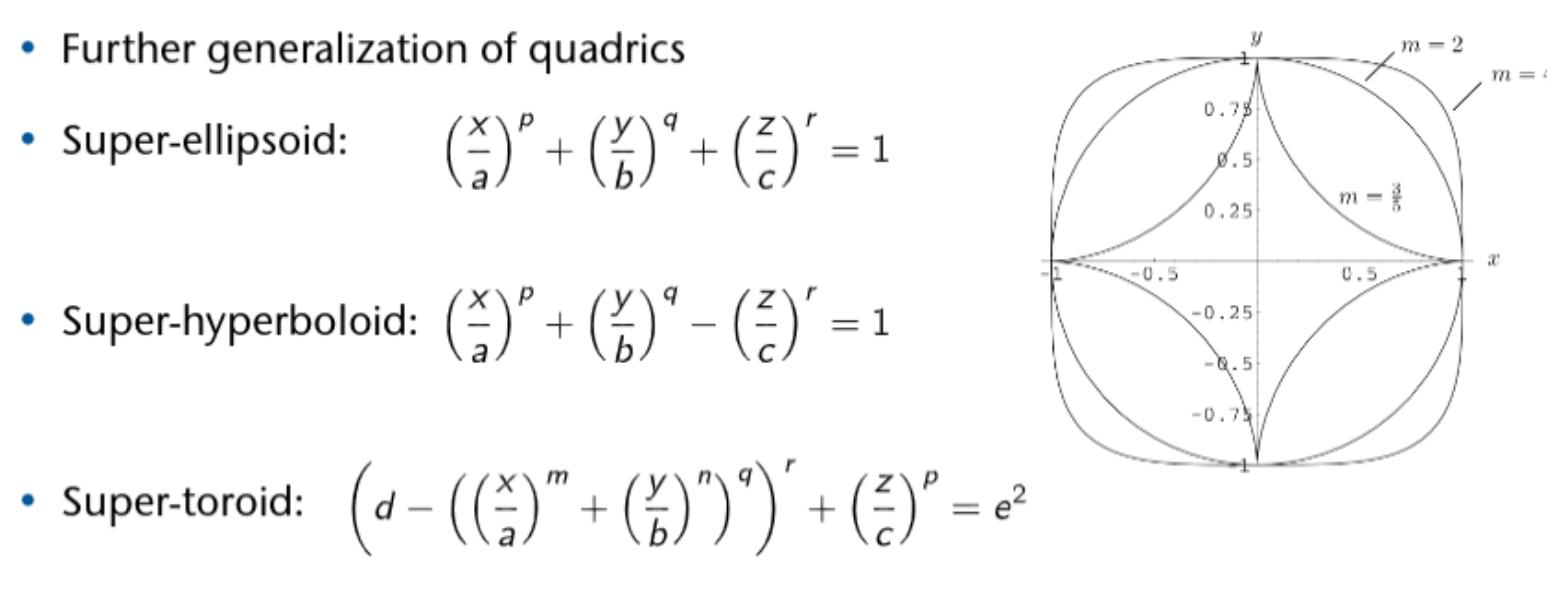
Quadrics

Implicit Surfaces
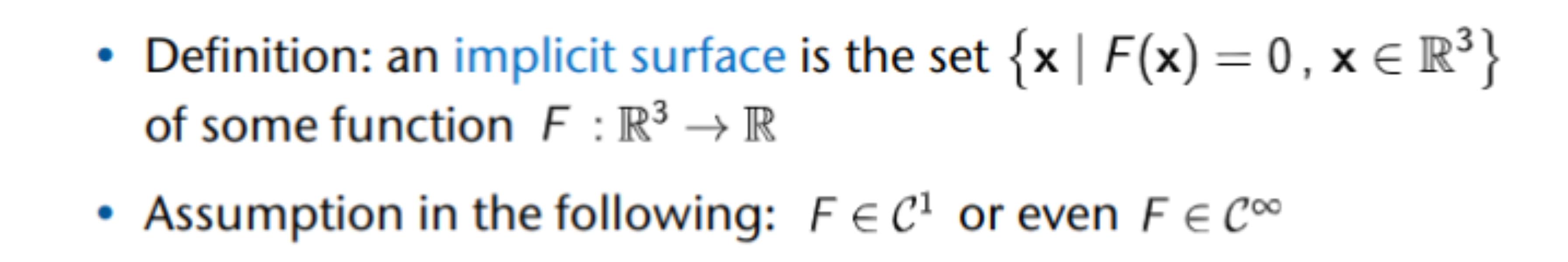
Metaballs

The Normal on Implicit Surfaces
⇒ The gradient of the field is the normal
Marching Cubes
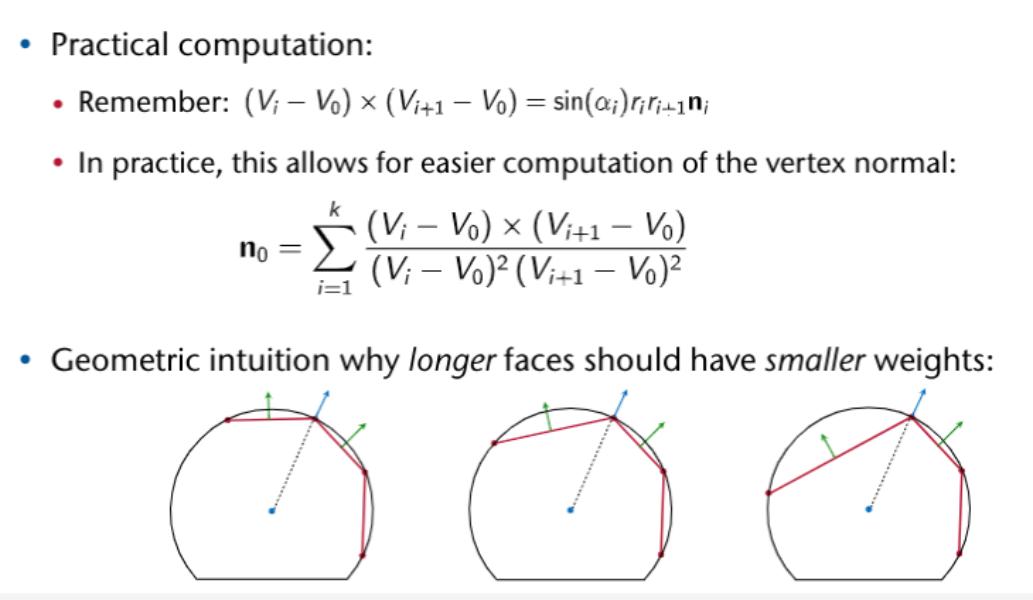
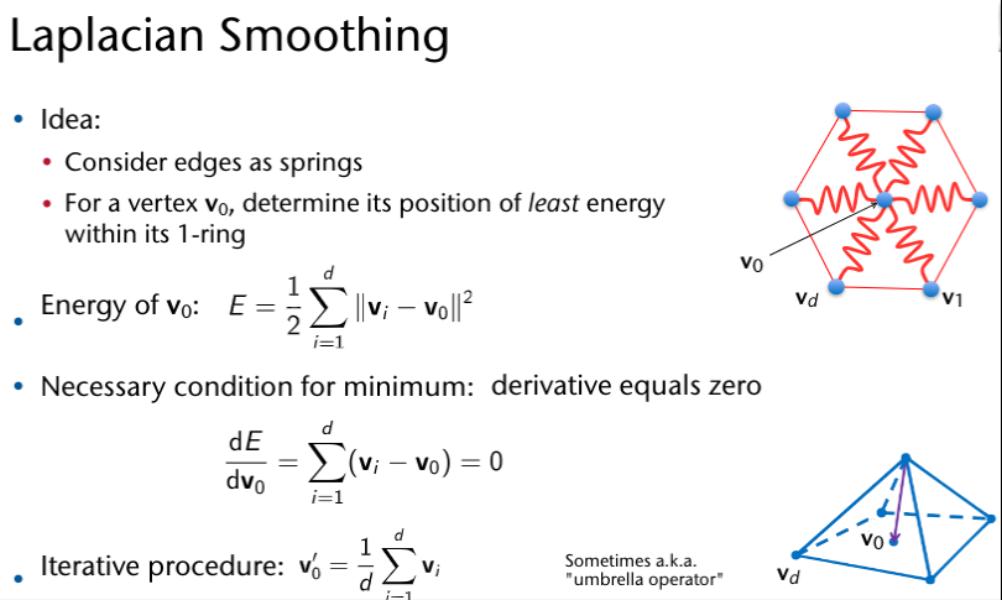
Weighted Moving Least Squares Method
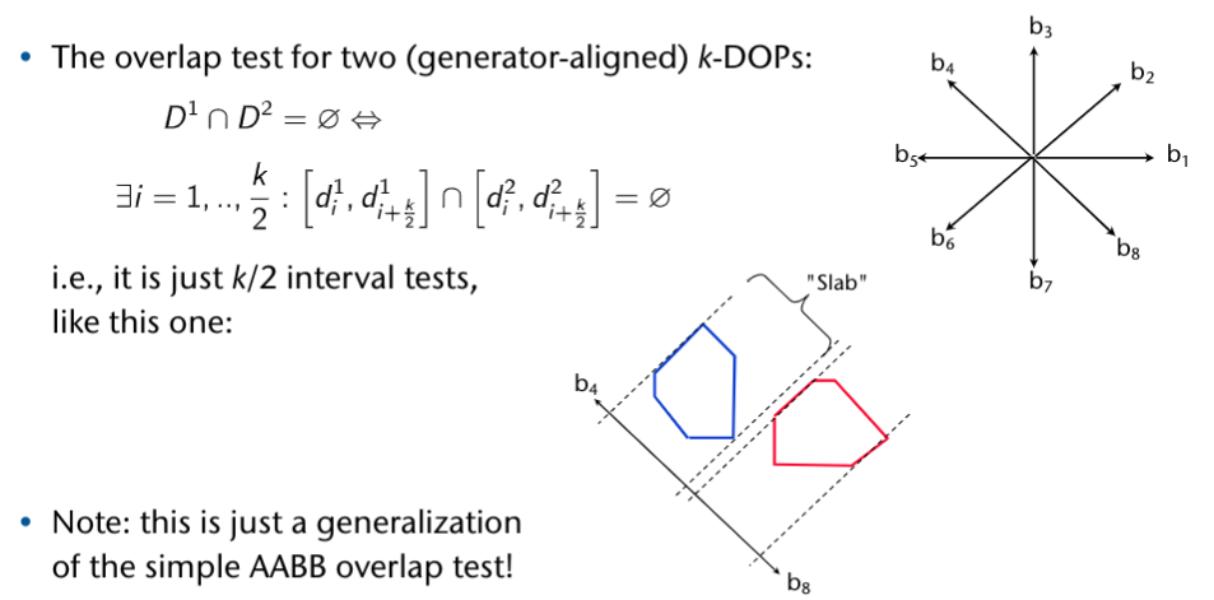
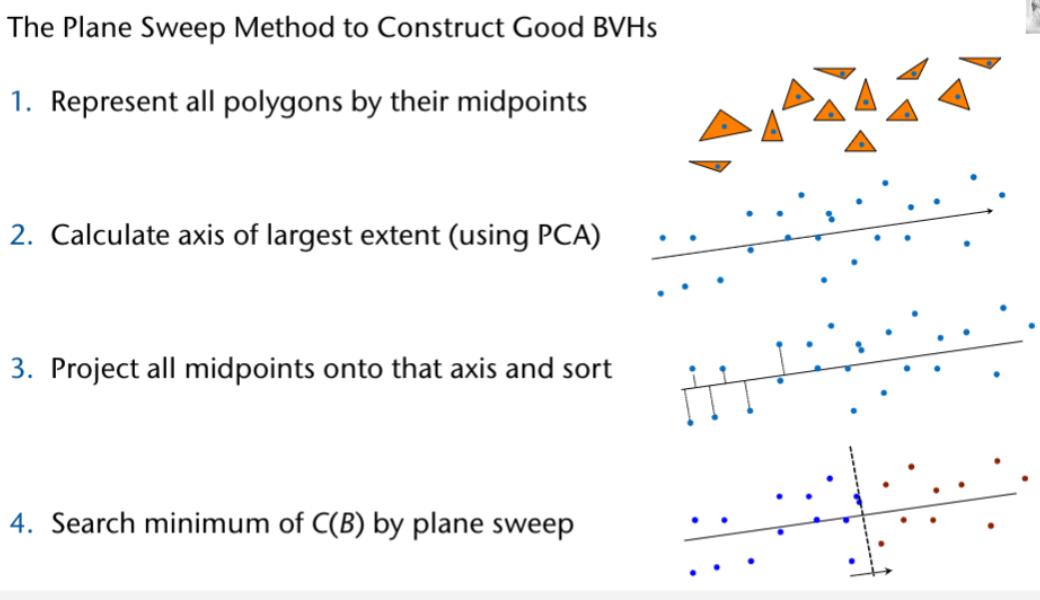
Acceleration Data Structures
Regular 3D Grids
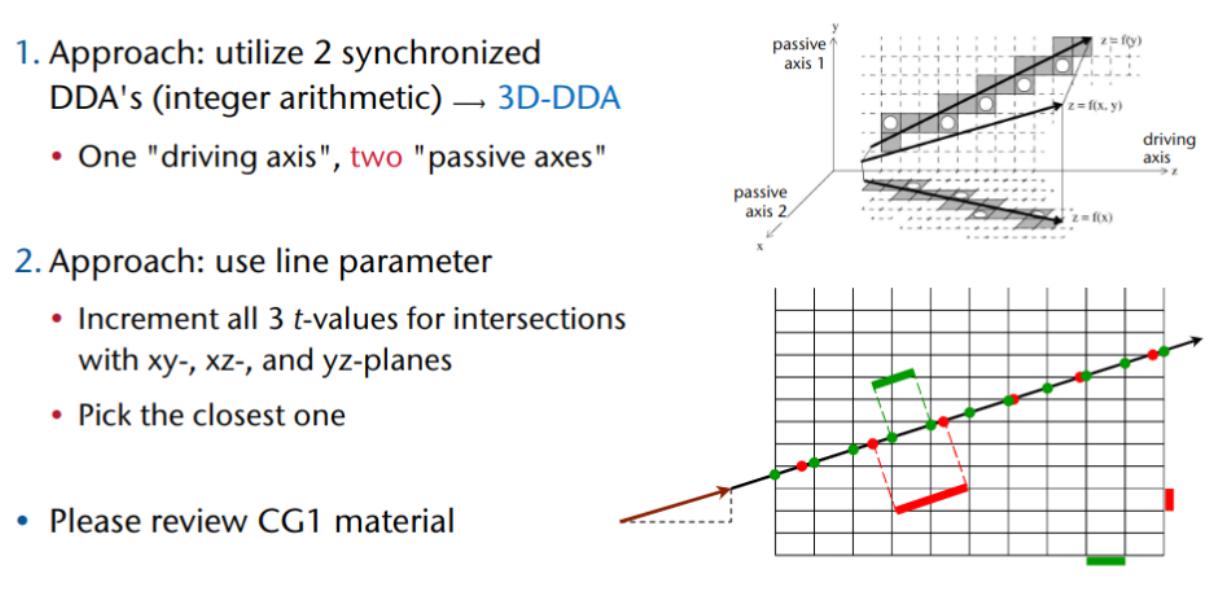
The Optimal Number of Voxels
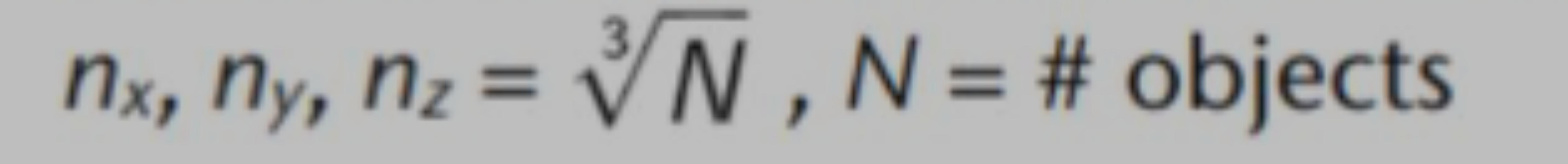
Mailbox Technique
Problem: Bei Spatial Hashing kann es passieren das ein Ray mehrmals gegen ein Object getestet wird.
→ Gib jedem Ray eine ID (Counter)
→ Vor jedem interesction check teste ob teste ob der Punkt (das t) aus der Mailbox geladen werden kann.
→ Wenn nicht speichere den Punkt (das t) mit der Ray ID in der Mailbox
Optimisation: Ein Hash Table per Ray
⇒ funktioniert parrallel
Hierarchical Grid
Irregular Grids
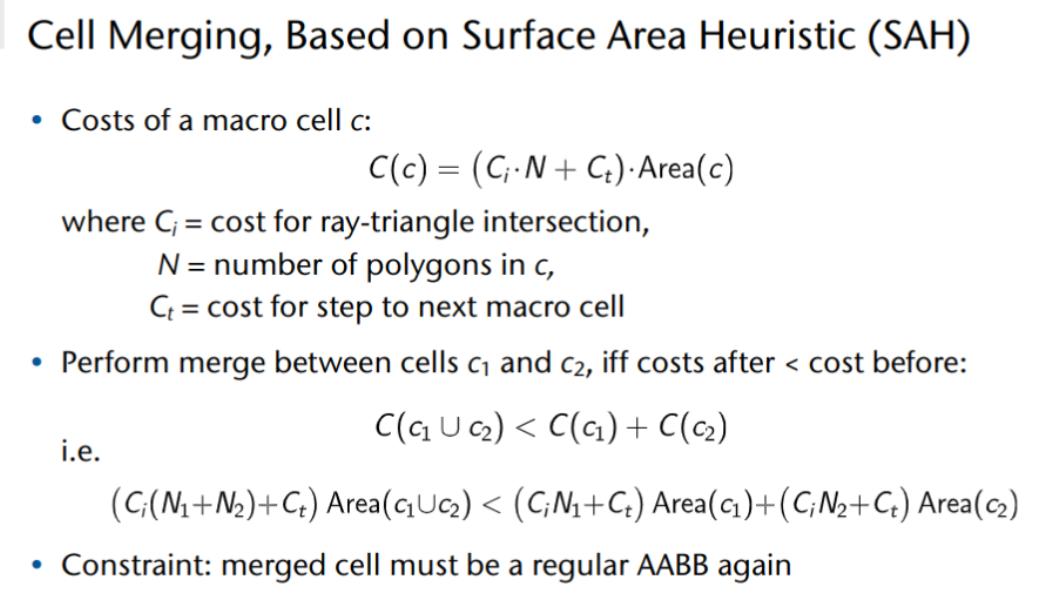
Octree
kD-Trees
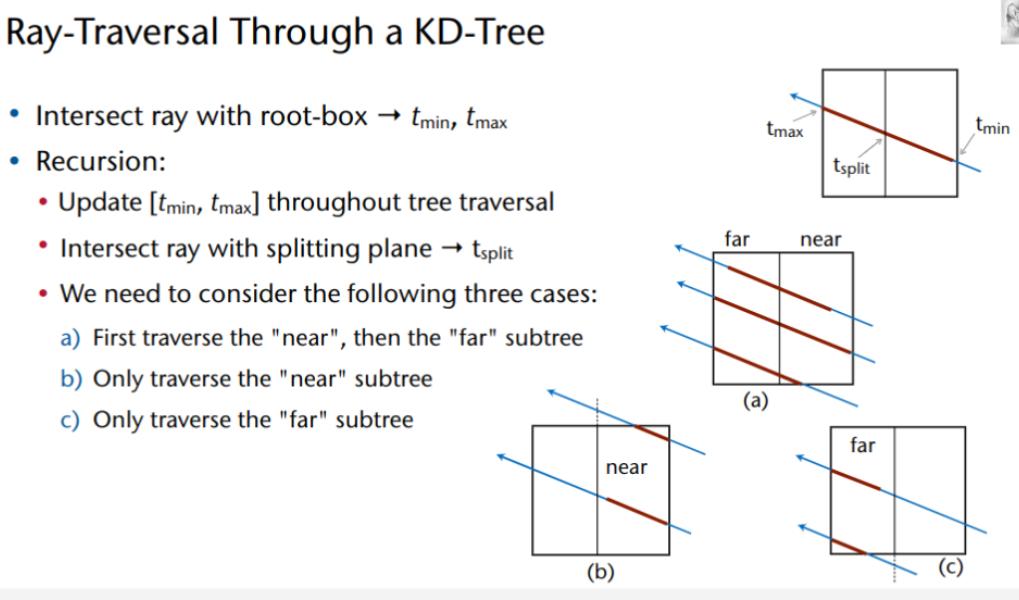
Finding a splitting plane
kD-Tree Splitting Plane
K-D tree Surface Area Heuristic
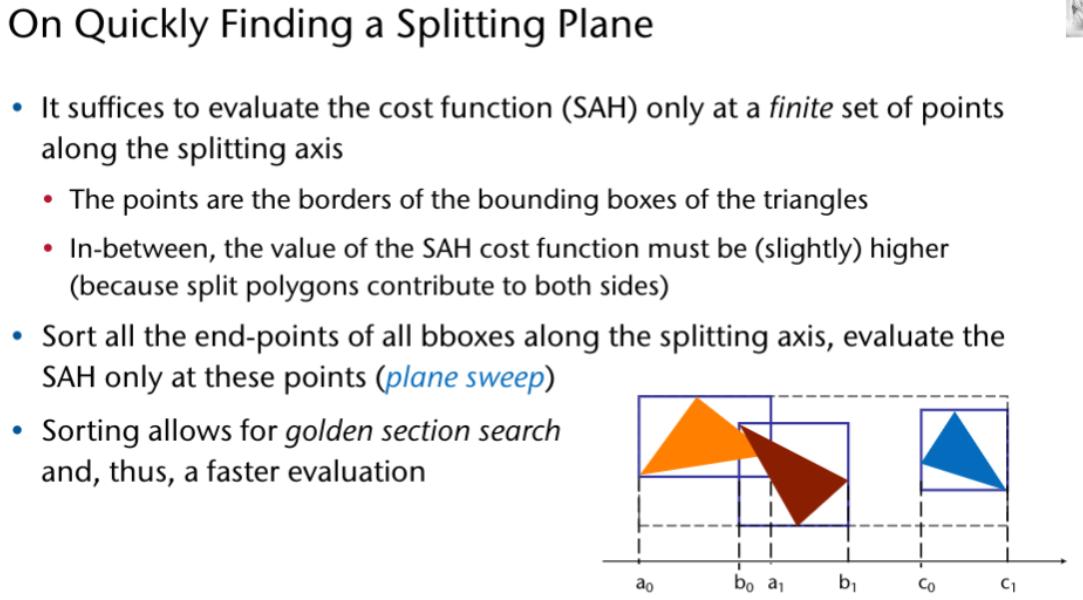
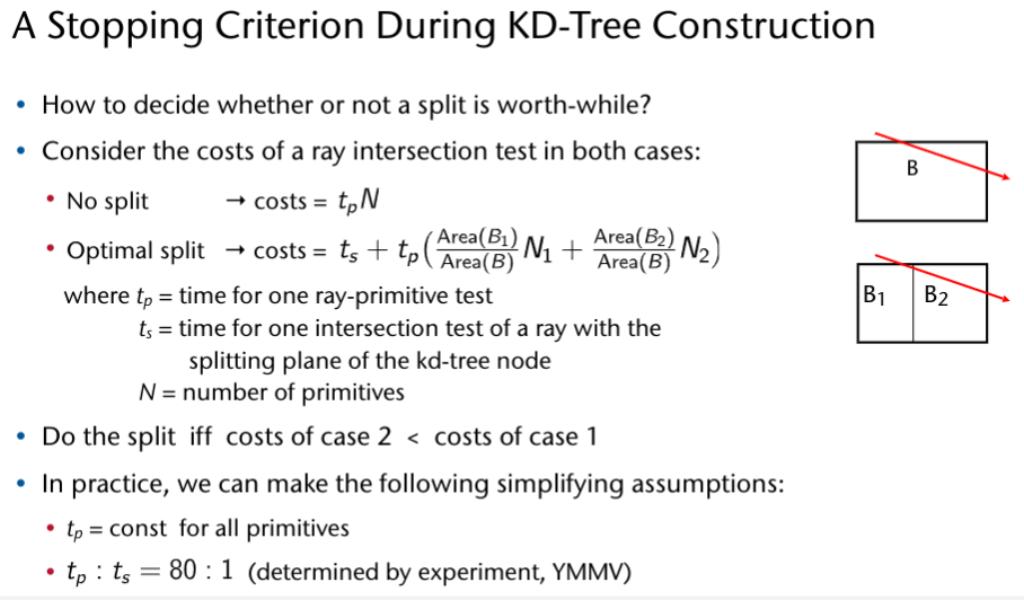
Laufzeit:
Running time:

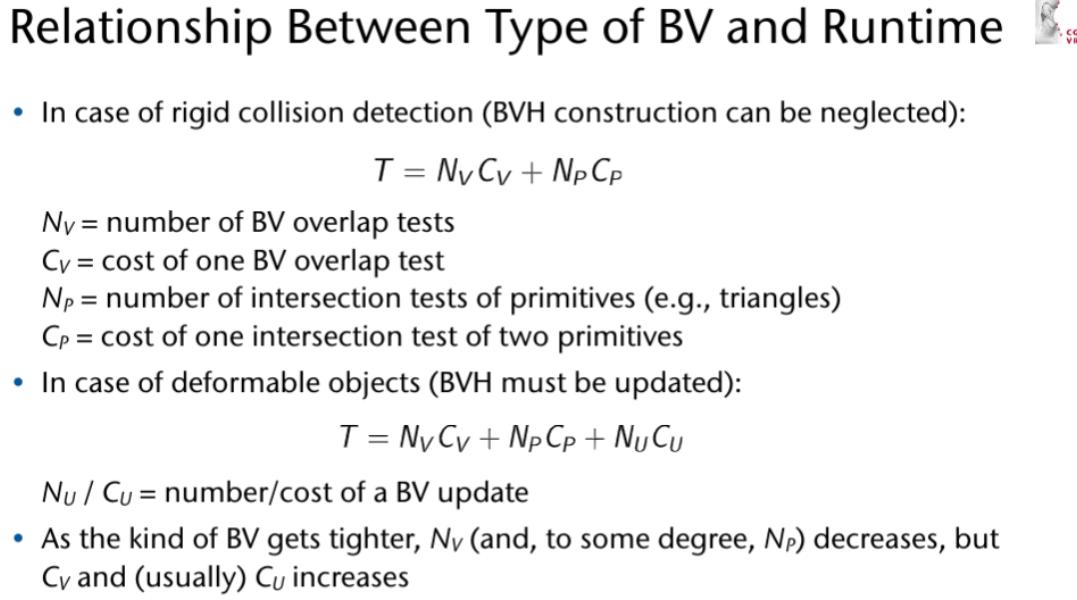
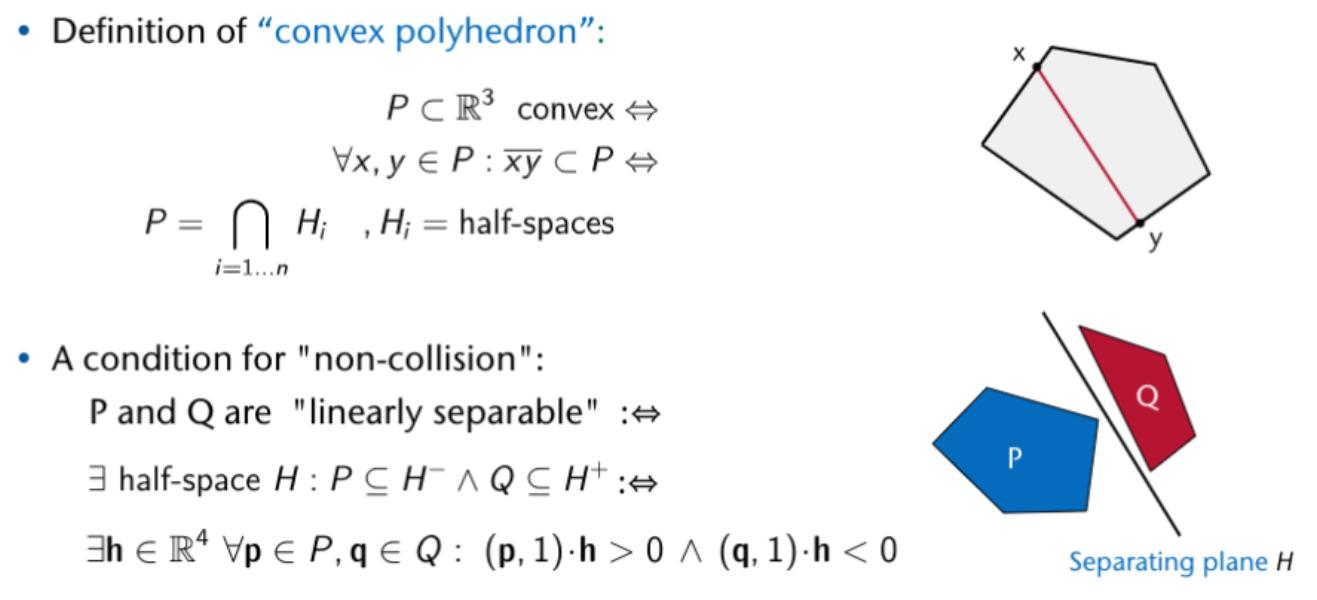
The Collision Detection Pipeline
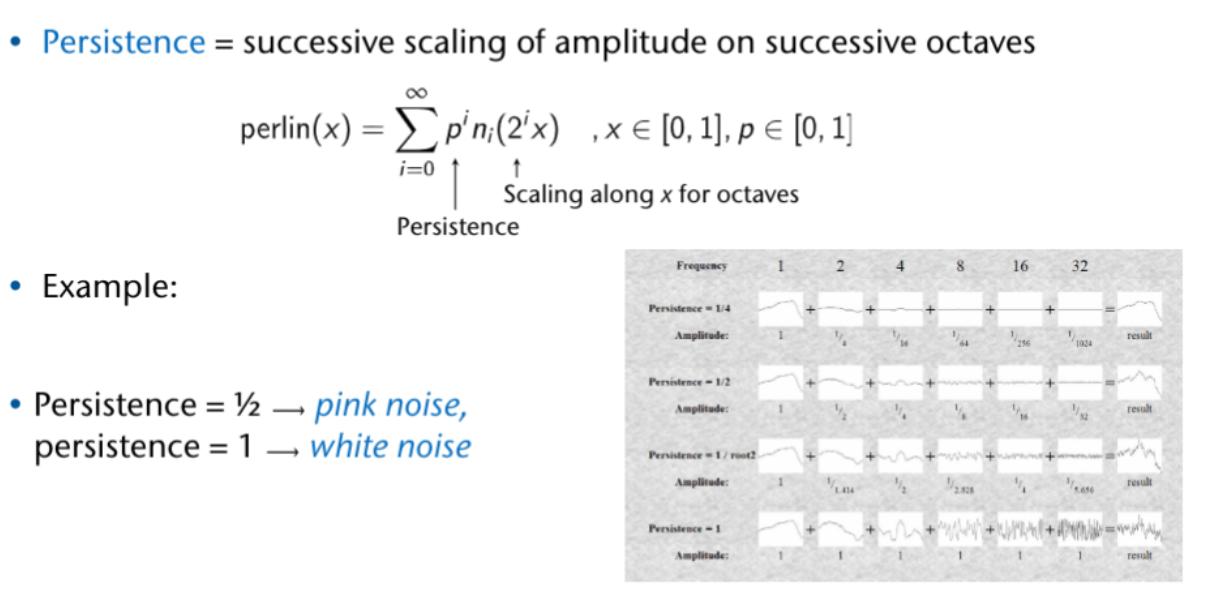
Voronoi Noise
Variations
Ambient Occlusion
1- Methode
Sample point in second renderpass in G-buffer (on fragment)
2. Methode
Average all pixel colors of neigbor positions in worldspace.
Flux
how much energy flows from/to/through a surface per unit of time.
Link to original
Symbol: Φ
Units = Watt
Irradiance
energy density = flux per area
Link to original
Lambert's law
Link to original
since:
Exitance
same thing as Irradiance, except for light leaving a surface
Link to original
Intensity
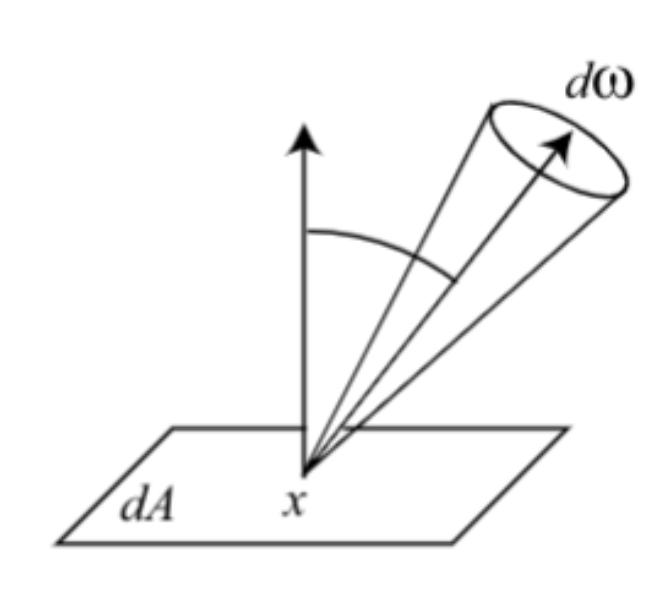
Flux over solid angles
Link to original
The Normal Distribution Function
Geometry Function
Fresnel Function
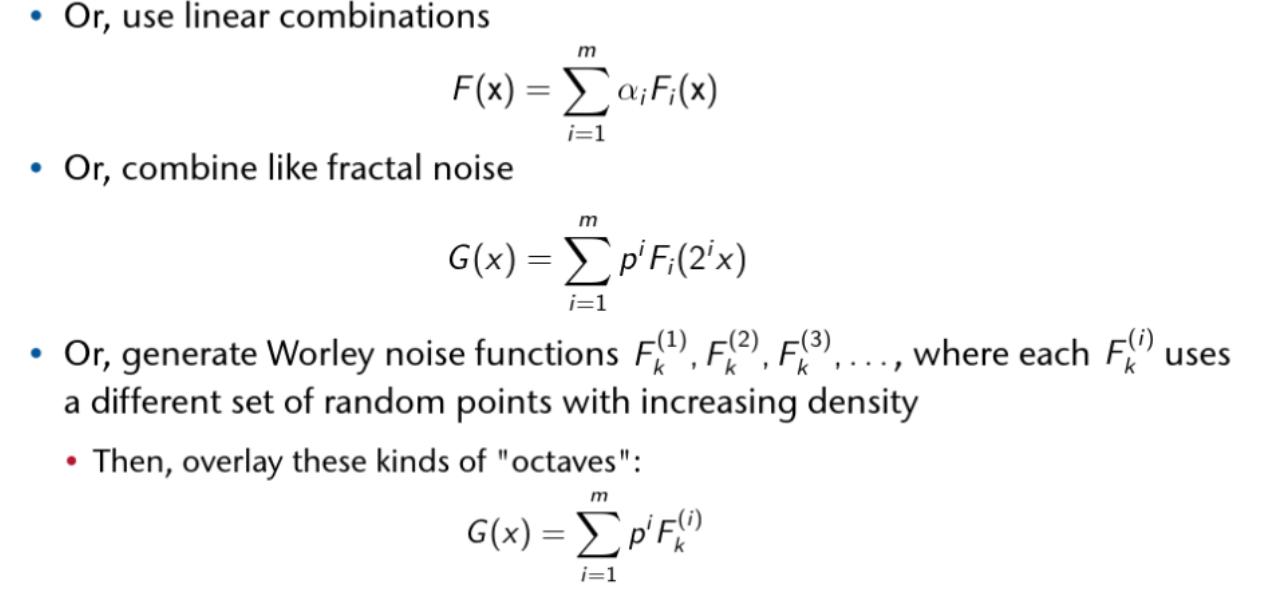
Subdivision Surfaces
The Catmull-Clark Subdivision Scheme

Homeomorphism
topology equivalent
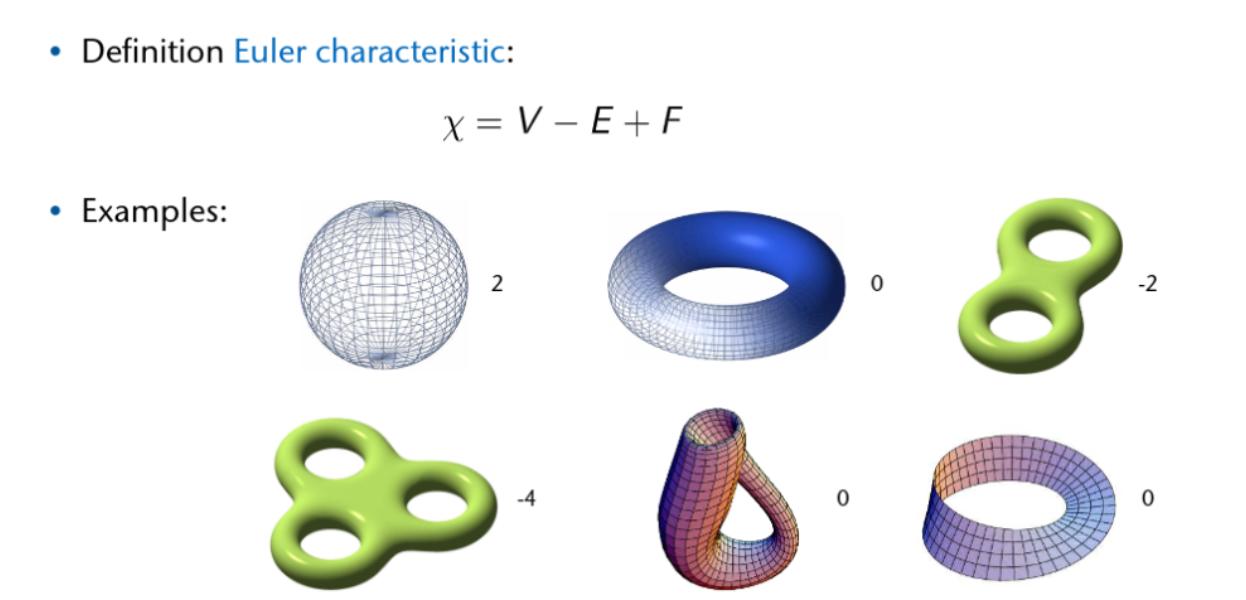
Two-Manifolds
A surface is called two-manifold if for each point on the surface there is an open ball such that the intersection of the ball and the surface is topologically equivlent to a two-dimensional disc.
-
closed
-
two-manifold
-
no -self intersection
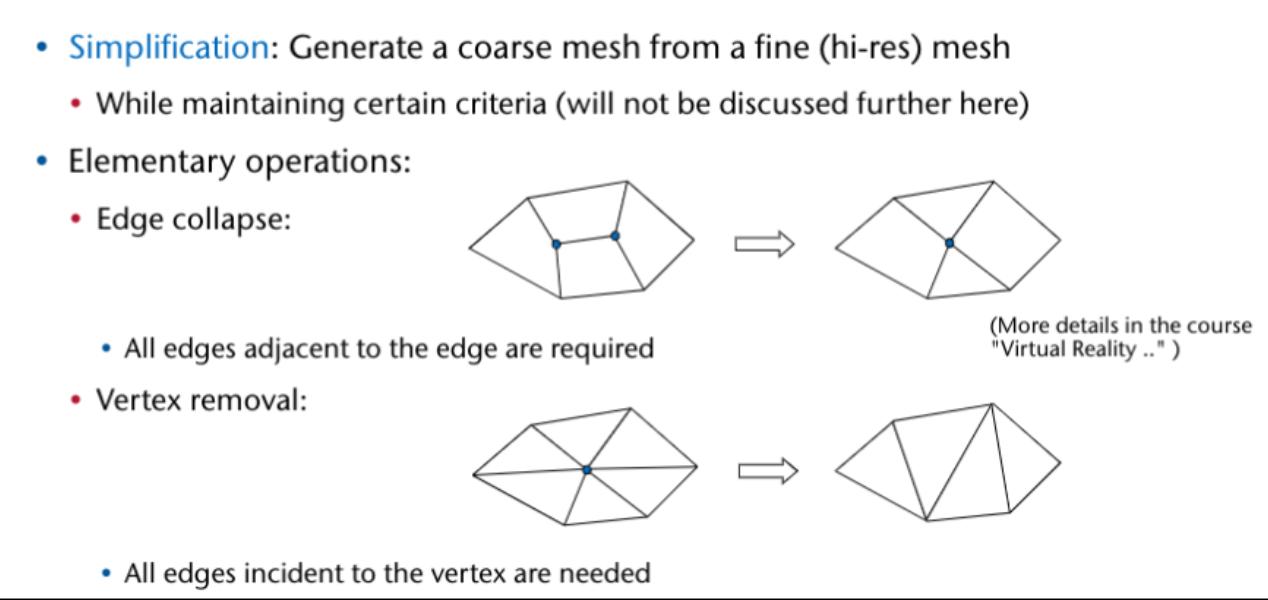
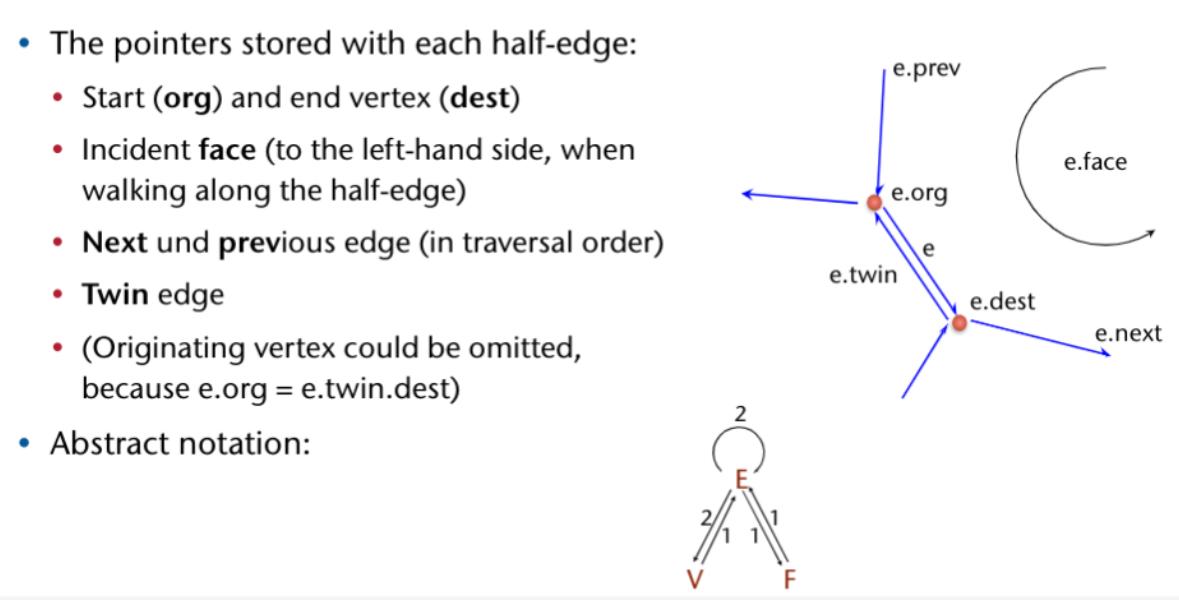
Potentielle Pürfungs Frage: Face gegeben → Alle Nachbar faces
-
Von Face zu Edge
-
Von Edge im kreis in dem man immer in Next geht bis man wieder beim start ist.
-
Bei jedem schritt in die Twin Edge gehen und das Face der twin Edge speichern.
Matrix Representation of Meshes
Regular Quad Meshes
Definition “regular quad mesh”:
Each face of the mesh is a quadrangle, and each vertex has degree 4.
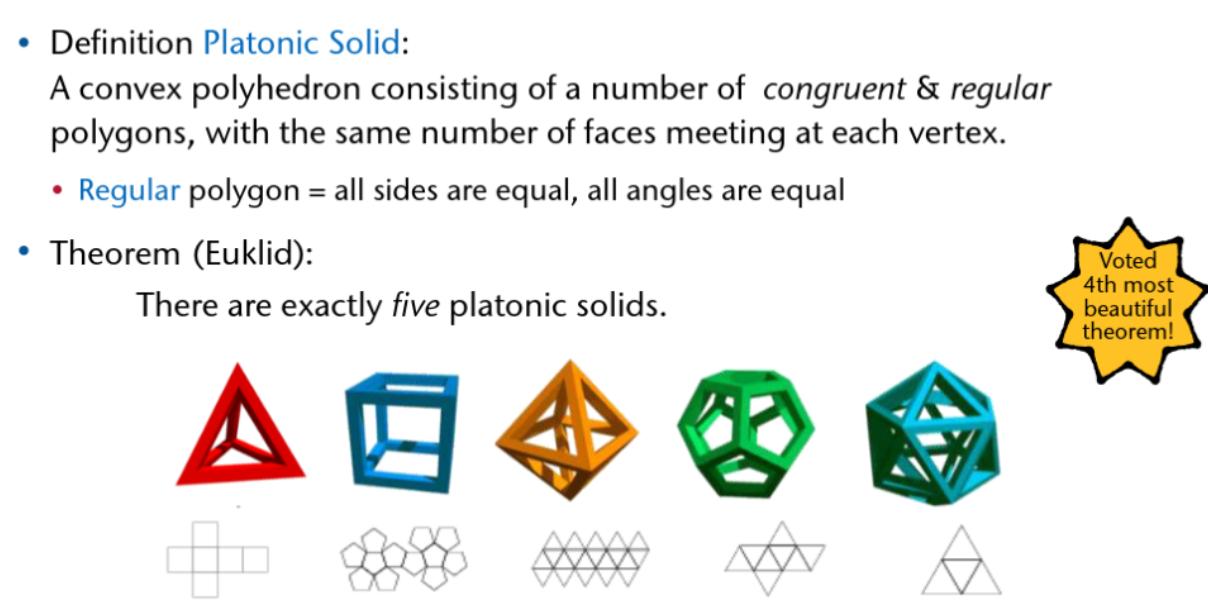
Regular Meshes
A regular (n,m,g)-mesh is
-
a closed,
-
orientable mesh,
-
with genus g,
-
where each facet has exactly n edges,
-
and each vertex has exactly degree m.
Parameterization

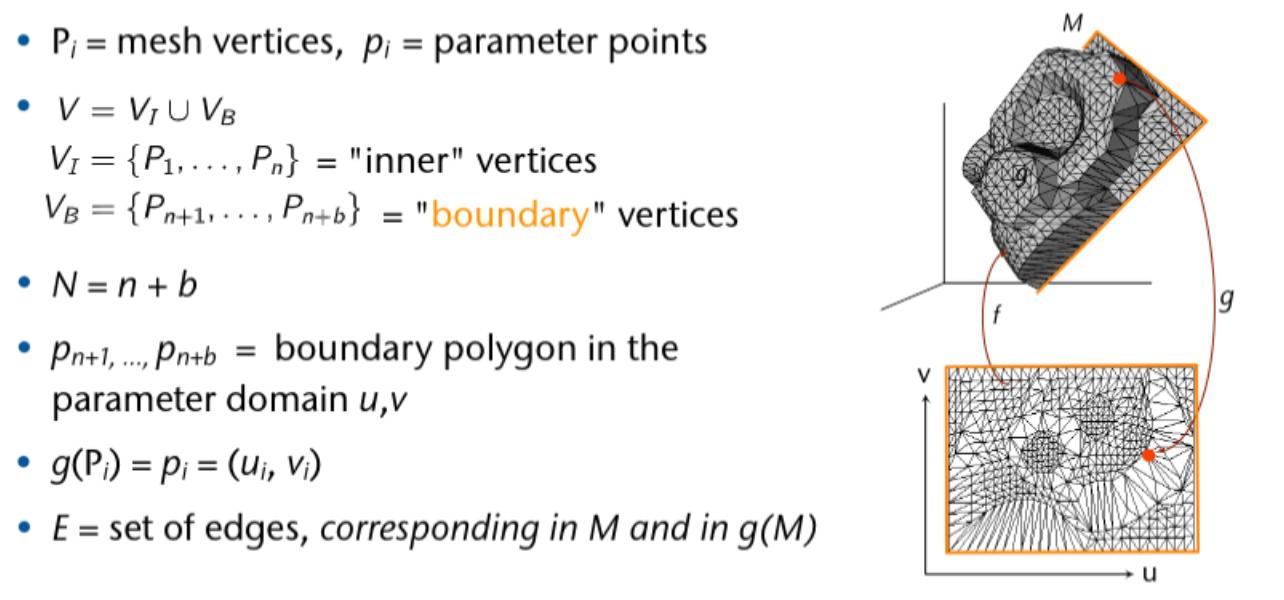
Parameterization Lamdas



Perform Step