What is Localization?
Given: Map (model) of the environment.
Task: Estimate the robot pose relative to the given map.
Robot pose:
- position (xR, yR)
- orientation θ.

Typs of Localization
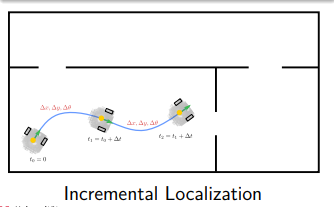
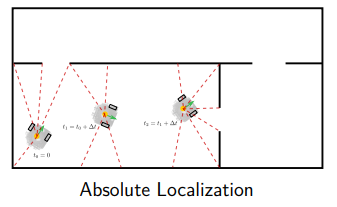
with mapping ⇒ SLAM
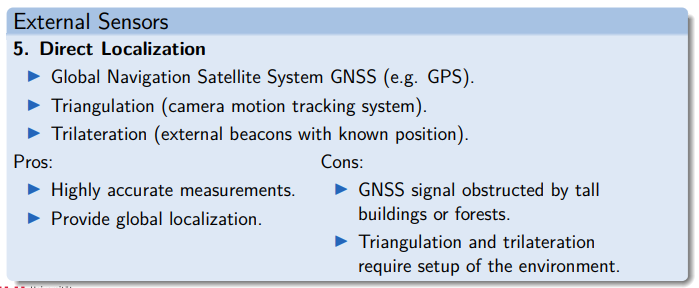
Sensors for Localization
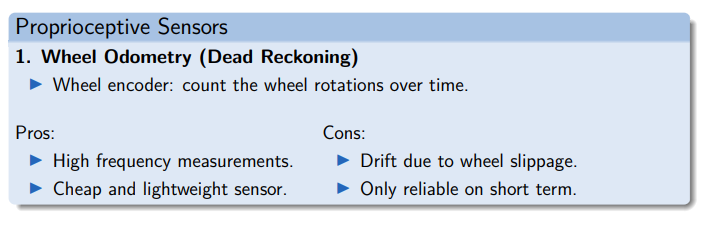
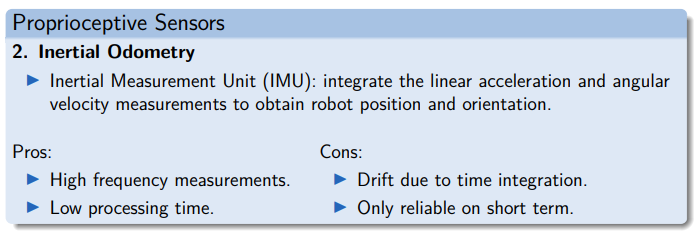
Proprioceptive Sensors
- Wheel Encoder → Wheel odometry
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) → Inertial odometry
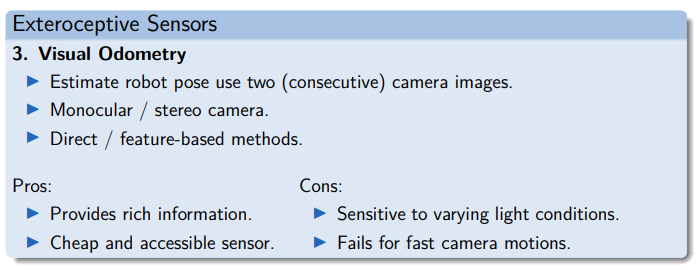
Exteroceptive Sensors - Camera → Visual odometry
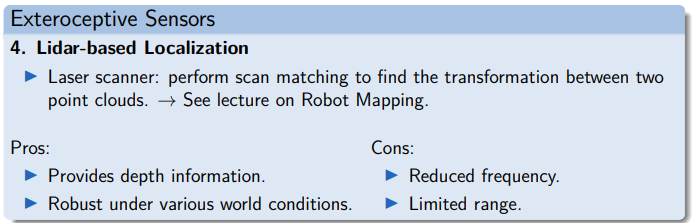
- Laser scanner, sonar → Scan matching (SLAM)
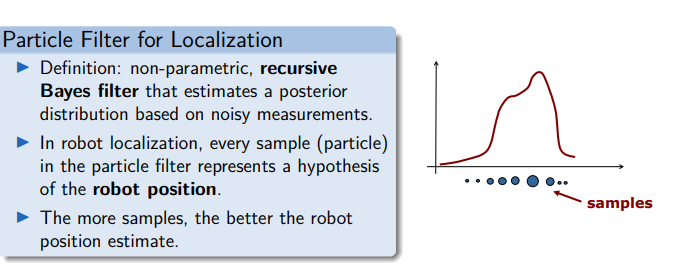
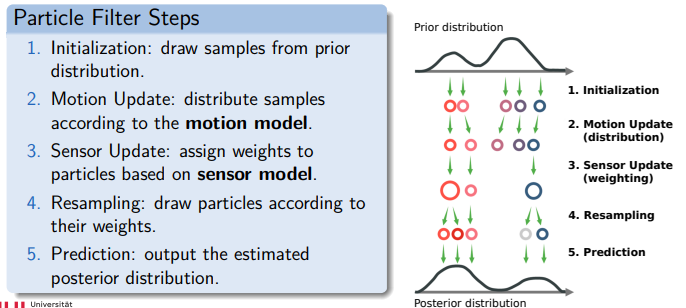
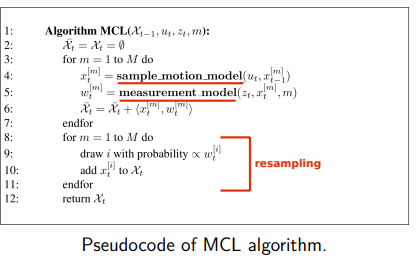
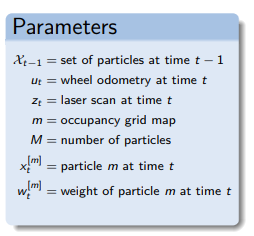
particle filter
Overview
Based on Bayesian statistics.
Methods: Kalman filter, particle filter (Monte Carlo Localization).
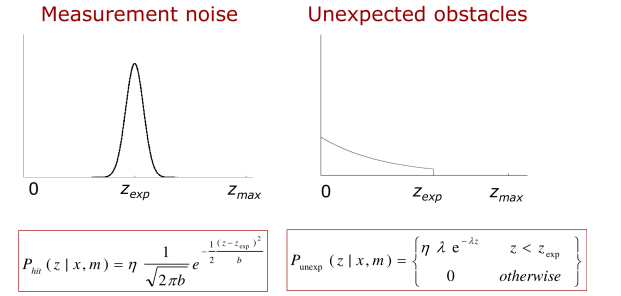
Sensors measurements: wheel encoder, IMU, GPS, laser scanner, camera, etc.Pros:
- Model sensor noise.
- Fuse multimodal sensor data.
Cons:
- Complex algorithms and models.
- Computationally expensive.
Function Approximation
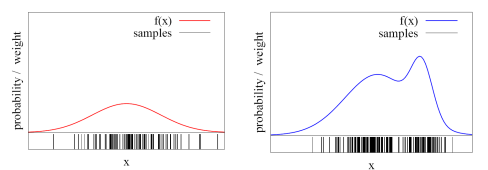
Probabilistic method used for non-parametric function approximation.
An arbitrary function can be described by a set of particles at time :
Pros
- Estimates any posterior distribution (i.e. not limited to Gaussian distribution).
- Able to cope with noisy sensor data and inaccurate odometry.
- Easy to implement.
Cons:
- Large number of particles slows down localization.
- Requires large storage space.
- High computational resources.
Further Problems
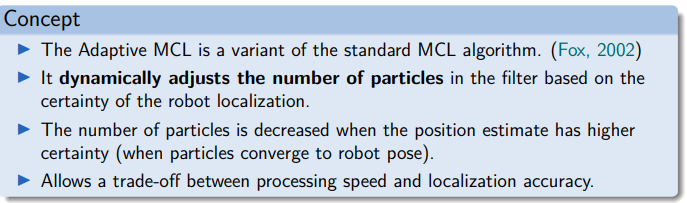
Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization
AMCL ROS Package
Link to original