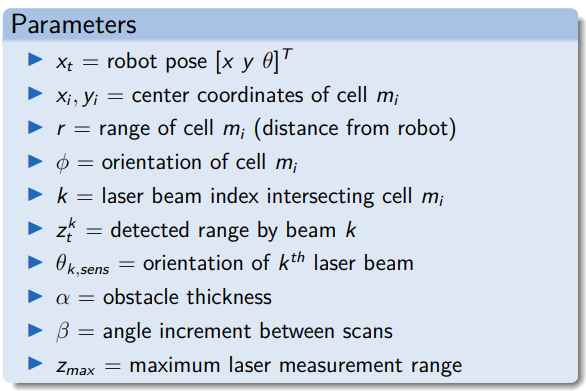
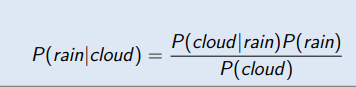up:: RDL MOC
lecture05-mapping-0.pdf
Grid Maps
Grid Maps
- Geometric model of the environment.
- The 2D world plane is divided into grid cells.
- Map cells can be free or occupied.
- The robot can only navigate in the free cells.
- It is a dense representation of the world. I Suitable for indoor environments.
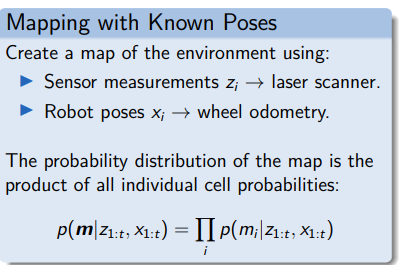
Occupancy Grid Maps
Binary cells
either free or occupied
Probabilistic cells
The cell occupancy is modelled by a binary random variable.
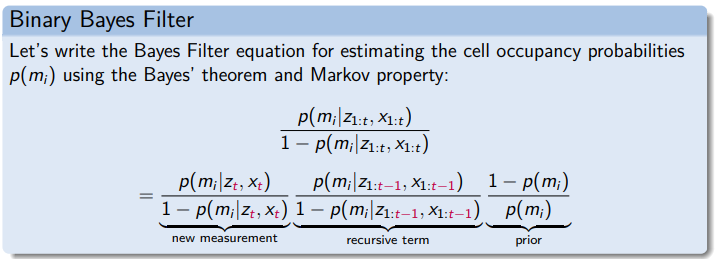
Map occupancy probabilities:
- Free cell:
- Occupied cell:
- No knowledge:
Assumptions:
- Cells are independent of each other.
- Range measurement only depends on current robot pose (Markov property)
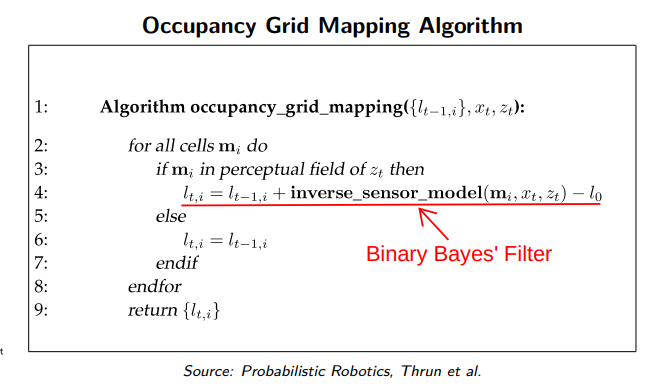
Algorithm
Possible states
- p_occupied
- p_prior (unchanged)
- p_free
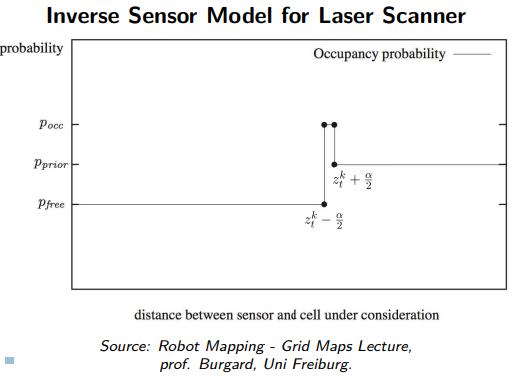
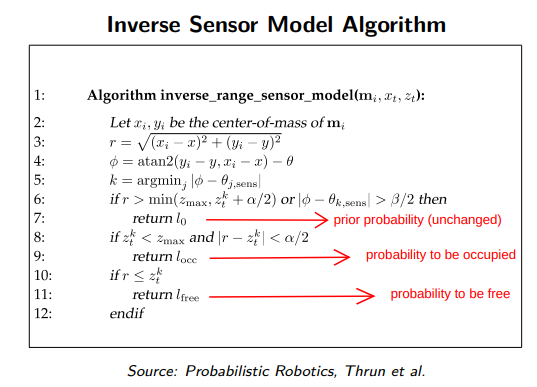
Inverse Sensor Model
Link to original
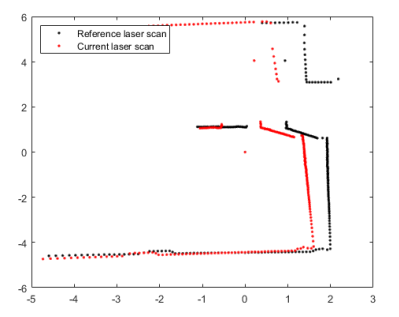
Scan mapping Algotithm
- Incrementally align two consecutive laser scanner measurements.
- Stitch the laser scans to create a map.
- The transformation between two measurements is used in robot Localization.
Example: Interactive closest Point
Link to original
Feature Maps
Feature Maps
Link to original
- The environment is represented by a set of observed features.
- Features are obstacles in the world identified by sensor readings (e.g. laser scanner, camera).
- The robot navigates based on the distance and heading w.r.t. the features in the map.
- It is a sparse representation of the world.
- Suitable for outdoor environments.
Loop closure
Loop closure
- Loop closing is the task of deciding whether the robot has returned to a previously visited area.
- Used in SLAM to correct the drift in mapping and localization.
- Approach: identify features that have been perceived in the past.
- When a match (i.e. loop closure) is detected, update the previous map and position estimates.
used in Grid Maps
Link to original
Bayes’ Theorem
Bayes’ Theorem
⇒ probability of hypothesis A given data B
(posterior belief distribution)⇒ likelihood of data B given hypothesis A
⇒ independent probability of hypothesis A
(prior belief distribution)⇒ independent probability of data B
Example
Bayes Filter
Probabilistic method to estimate an unknown probability density function (PDF) recursively over time using incoming sensor measurements and a mathematical process model.
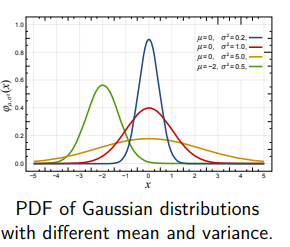
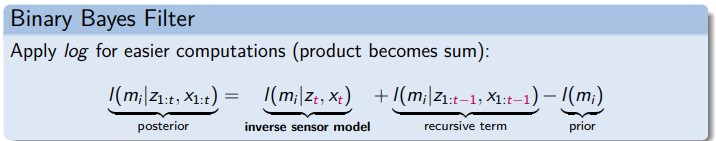
Binary Bayes Filter
Probability density function (PDF) of a binary variable.
Task
Cleaning
Resteraunte
Security
Grid based mapping
Challenges
Fast Moving Objects
Von Sensor Daten
Link to original
ROS2 Mapping Libraries
ROS2 Mapping Libraries
Link to original
- SLAM Gmapping
- Hector SLAM
- Published by TU Darmstadt in 2011
- It performs fast online learning of occupancy Grid Maps.
- Low computational resources.
- Uses Lidar and IMU data, but no odometry.
- SLAM without Loop closure.
- Link: http://wiki.ros.org/hector_slam
- Cartographer
- Published by Google Research in 2016.
- It works with a variety of sensor configurations (e.g. Lidar, IMU, cameras).
- It implements the scan matching algorithm.
- It performs local and global SLAM (Loop closure).
- Link: http://wiki.ros.org/cartographer
- SLAM Toolbox
- Published by Steve Macenski et al. in 2021 and is currently the supported ROS localization and mapping package.
- Maps large and dynamic spaces.
- Able to continue mapping from prior sessions.
- Implements Loop closure.
- Link: http://wiki.ros.org/slam_toolbox
next: RDL VL 06 Localization