up:: RDL MOC
lecture11-mechanical-design-0.pdf
What is Mechanical Design?
The design process of mechanical components and systems
(natural and artificial)
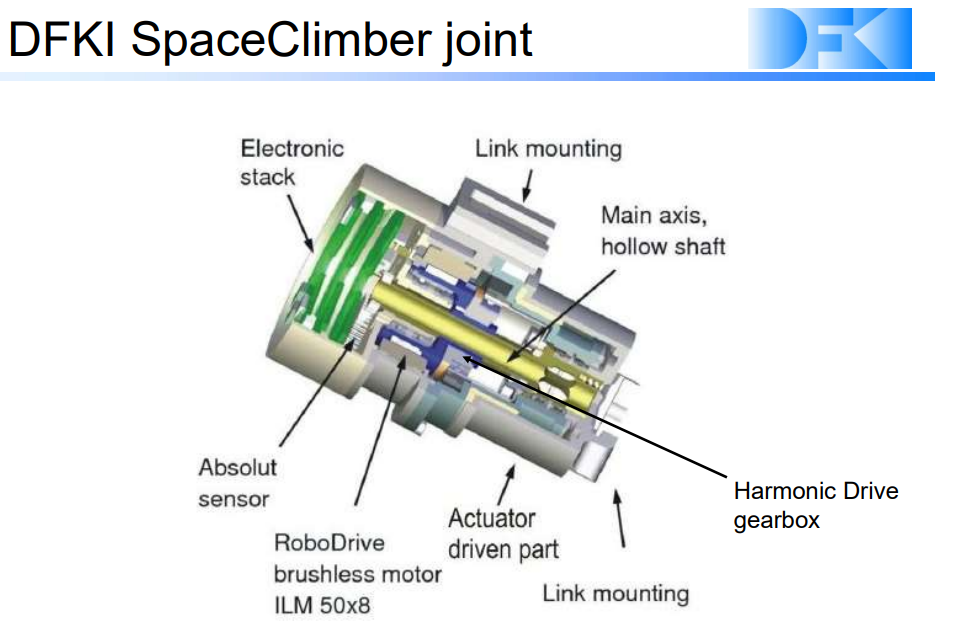
also see: Robots at the DFKI
Three steps involved in mechanical design
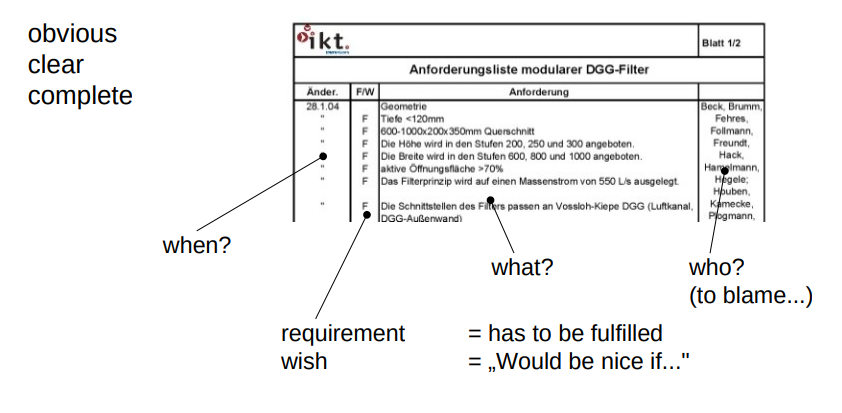
Specifications
Principles
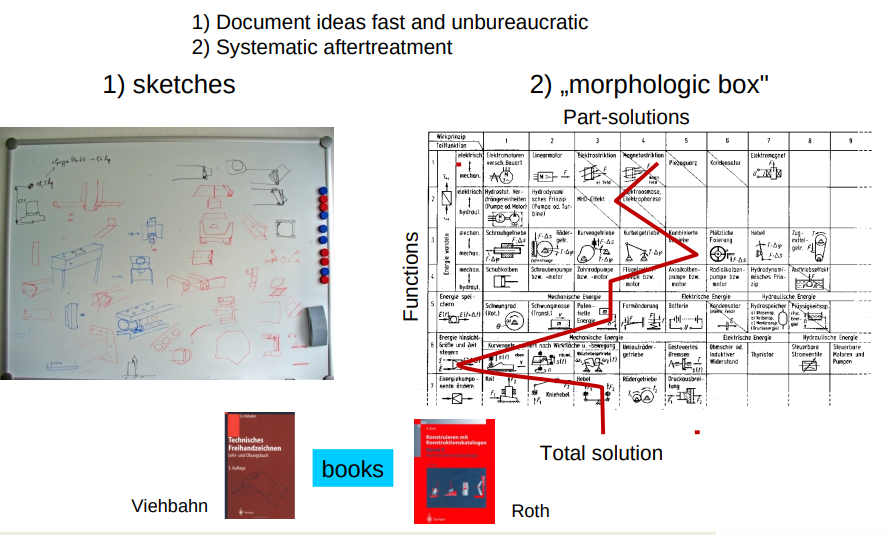
Design
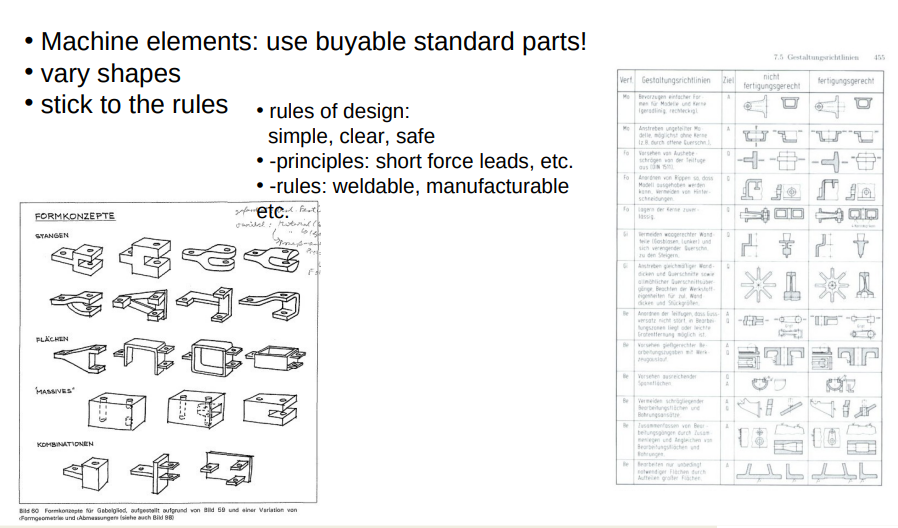
Machine Elements
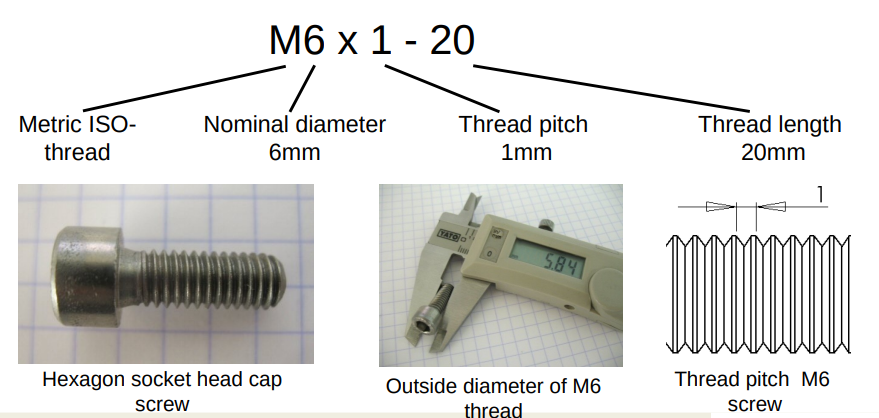
Screws
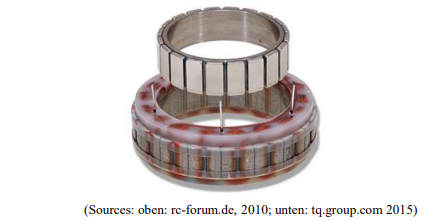
Bearings:
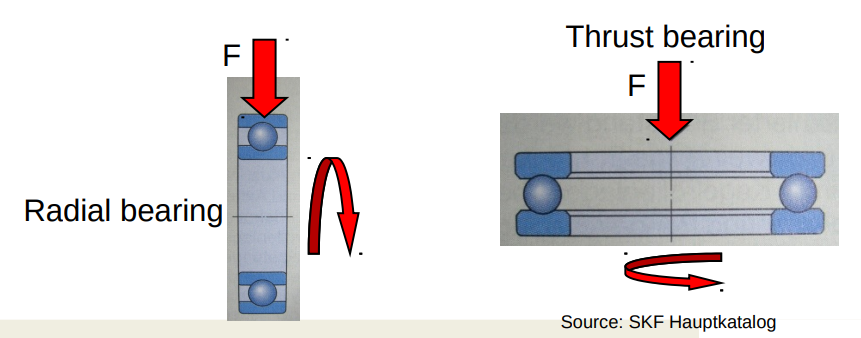
- Balsl for high revelotions
- Zylinder or Neelde for high Forces
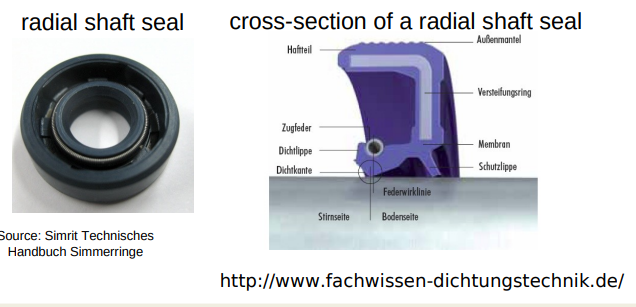
Sealings (O-Rings)

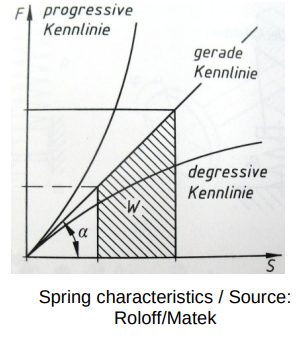
Springs
Hooks Law
Spring force [N] = spring rate [N/mm] x spring travel [mm]Link to original
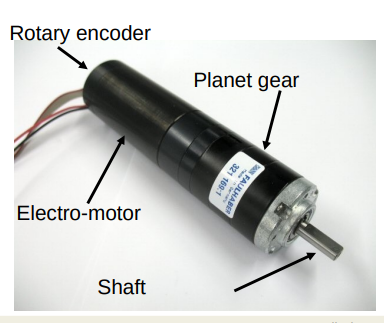
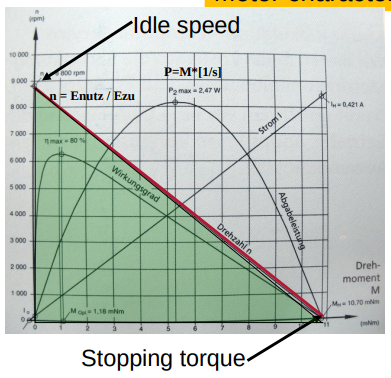
Motors
Motor
Example
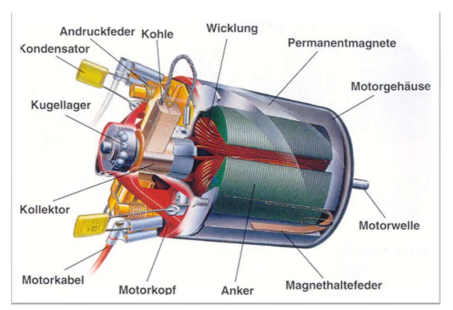
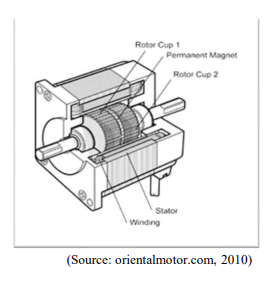
Direct current motors (DC-motors)
- Up to 98% efficiency
- Power cord or battery
Brush motor:
- cheap
- Mature technology
- Sparking / high-frequency interferences
- Life limit – carbon brushes
Brushless motor:
- More efficient / less heat
- Less wear
- More power per weight
- Requires a controller
Stepper Motors
Revolutions will be made in an amount of steps (degree), not as a constant movement, exact positions can be achieved
Bipolar: 2 coils 4 connections (more power per motor-volume)
Unipolar: at least 5 connections, simpler control
Reluctance motor
- toothed soft iron structured rotor
- No permanent magnets
- Free magnetic flow, no magnetic field after switched off
Permanentmagnet motor
- Permanentmagnet on the shaft / Stator made of soft iron
- Moment of rest
- Lower resolution in comparison to ther reluktance motor
Hybridmotor
Permanentmagnet and toothed soft iron core on the shaft
Servos
- Analog servos
- Low power consumption
- Low price
- Digital servos
- Faster positioning time
- Higher resolution
- Partly programmable
- PWM-control
Common for hobby servos
Servo elektronics regulate the actor (potentiometer) against the motor position
The pulse width of the control signal regulates the target position
Various variations on pulse widths and travel ranges
Link to original
Desing
qualitative design
(norms, shapes etc.)
⇒ Knowlage about desing
quantitative design
(material, strength, stiffness, other desired parameters.)
⇒ Desinging something in a way it can’t fail
- if you have to calculate, the construction is not good.” → Observe proportions.
- Roughing calculations – survey orders of magnitude

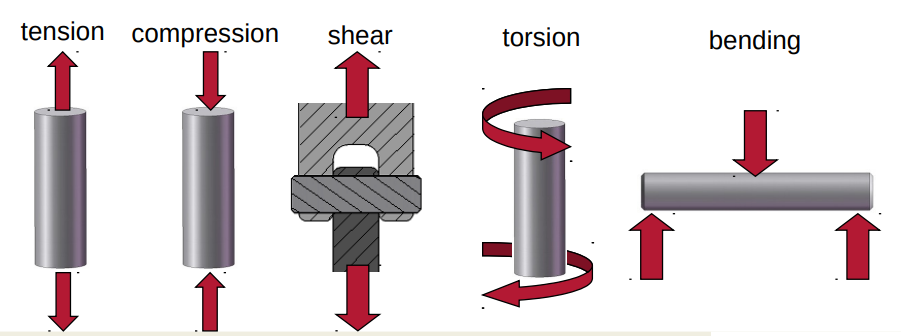
Loads
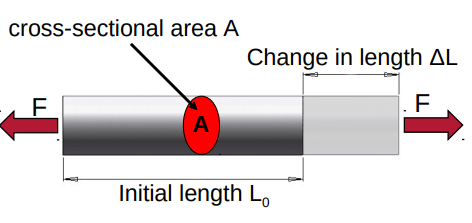
Elastic range
components behave like a „spring“
tension [N/mm2 ] = force [N] / cross-sectional area [mm2 ]
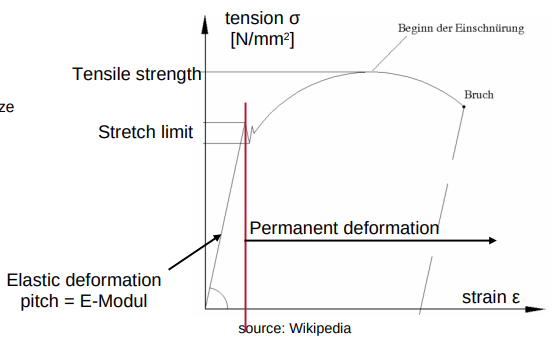
Plastic range
components deform permanently
elongation = change in length [mm] / initial length [mm]
E-modulus
The relationship between tension and elongation is called the elasticity modulus
Modulus of elasticity [N/mm2 ] = tension [N/mm2 ] / elongation
Additive and subtractive manufacturing processes
Additive
- 3D printer
- Laser sintering (SLS)
- Welding
Subtractive
-
Sheet cutting
- Laser cutting
- Plasma cutting
- Water-jet cutting
-
Milling
Biomimetics
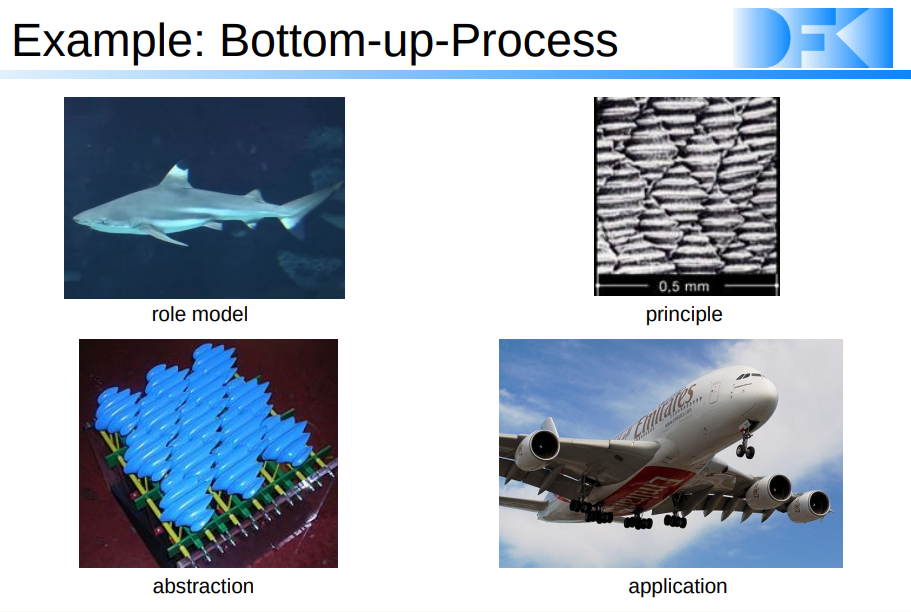
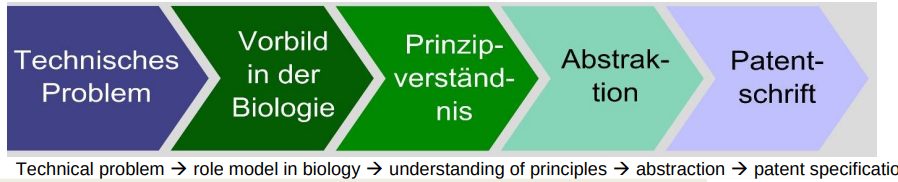
Bottom-up-Prozess
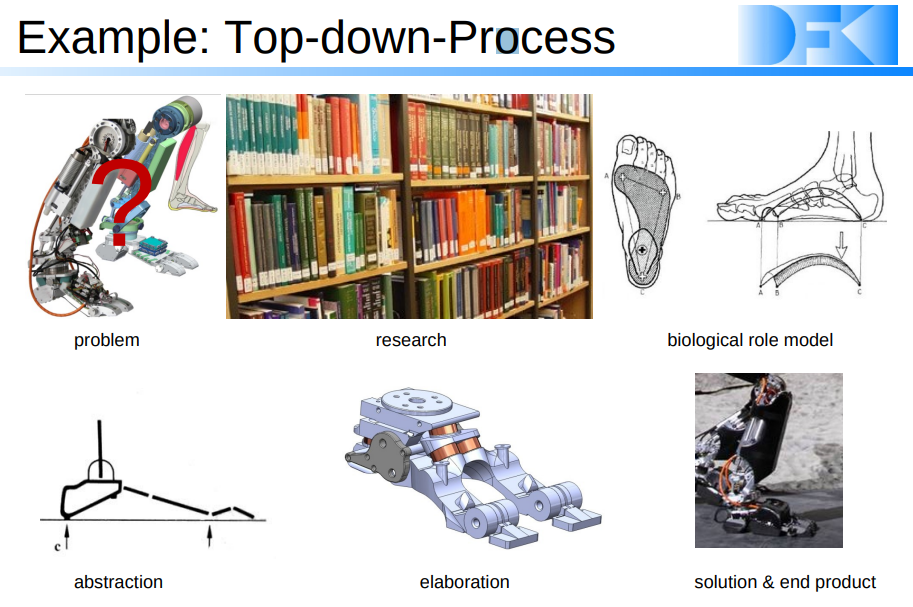
Top-down-Prozess
Link to original
Good Books
- Warum alles Kaputt geht
- Tabellenbuch Metall
next: RDL VL 12 Actuators